
Why Use Creative Commons Licences in Uganda
The Licences are key tools in enabling Uganda achieve universal access to knowledge goods such as access to information for health, education or literacy. This is because the producers of knowledge goods, who are mostly advanced economies, are increasingly expanding an intellectual property right...

Creative Commons Public Domain -Luganda Brief
Creative Commons (soma kuliyetivu komonizi) kitongole ekiri ku ddala ly’ensi yonna ekyobwanakyewa ekyewaayo mubumaliririvu
okutumbula okumanyisibwa okuyitira kumitimbagano gy’ebyuma
bikalimagezi okutali kusasulire, okuwagira okukozeseza, awamu
n’enkola eyokugabana ewatali bukwakkulizo amagezi ...

Creative Commons Luganda Translations -Six Licences
Creative Commons is a nonprofit organization founded in the United States of America to enable people to share and give permission for use of their creativity and knowledge through free legal tools.

Regulation of tobacco use in Uganda
The Tobacco Control Bill 2012 has been introduced in Parliament as a private members Bill “to protect people in both the present and future from the devastating health, social,
economic and environmental consequences of exposure to tobacco smoke”. Basing on an assessment of tobacco exposure in a...

Influencing copyright law reform and promoting creative commons initiatives among library societies in Uganda
Because Uganda In April 1994 signed the Marrakesh Agreement establishing the World Trade Organisation (WTO), Uganda is required to ensure that her laws and regulations are brought to
conform to the Member States’ obligations under the Agreement.

The Parliamentary Motion on Maternal Health 15th December 2011
On 15 December 2011, the Parliament of Uganda adopted a landmark motion urging Government to address the country’s alarming rate of maternal deaths and, among other things, consider compensating the families of victims.
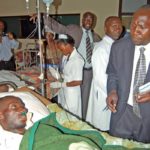
Human rights implications of load-shedding health facilities
Electricity is an essential service for personal and household use but more so for use at such public facilities as hospitals. Interrupting electricity supply through improper procedures, particularly through unannounced or unexpected load-shedding, poses a direct risk to the lives of patients wh...

Protection & Access
Uganda’s Industrial Property Bill (2009) needs to be reviewed before it is enacted into law,
to make full and maximum use of the flexibilities available in the TRIPS Agreement in order
to guarantee public health, particularly access to essential medicines, for all Ugandans

Rethinking the role of intellectual property policy in the HIV response in the East Africa Community
Provisions of the Draft Regional Intellectual Property Policy and Protocol on TRIPS Flexibilities
and Public Health should be used to improve the anti-counterfeiting legislations being
developed by the East African Community (EAC) and its member states. This will, among other
things, contribut...

Constitutional provisions for the right to health in east and southern Africa
The extent to which health rights are neglected or promoted is a major factor in the
promotion of health equity in Africa. Central to this is the incorporation of the right to health
in the national Constitution, as the supreme law of the country. Including the right to health
as a constitutio...
Anti-counterfeiting laws and access to essential medicines in East and Southern Africa
The countries in eastern and southern Africa and the East African Community are at
various stages of enacting laws to address counterfeiting. Counterfeiting is a problem for
public health if counterfeit medicines lack the active ingredients that make them
effective, or if they are harmful. Yet...
- « Previous
- 1
- 2
